|
|
Available in LEADTOOLS Imaging Pro, Vector, Document, and Medical Imaging toolkits. |
|
|
Available in LEADTOOLS Imaging Pro, Vector, Document, and Medical Imaging toolkits. |
Using the LBitmapBase::CreateFadedMask function:
When using the LBitmapBase::CreateFadedMask function, the general process is as follows:
|
1. |
Create an LBitmapBase object and use it to load an image. |
|
2. |
Set a region in the image using an LBitmapRgn object. |
|
3. |
Create another LBitmapBase object to hold the fade mask and call the function on the image’s object. The images below show various fade masks resulting from the use of various flags. For these images, the following values were also used: |
Region type: rounded rectangle.
nLength = 50;
nFadeRate = 15;
nStepSize = 3;
nMaxGray = 255;
crTransparent = RGB(255, 0, 0);
First: without using FADE_OUTER
1) No Flag
transparency
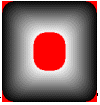
2) FADE_WHITETOBLACK
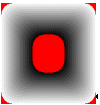
3) FADE_DUMPFILL

4) FADE_DUMPFILL | FADE_WHITETOBLACK
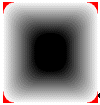
5) FADE_DUMPFILL | FADE_FILLCOLOR_START
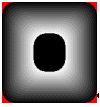
6) FADE_DUMPFILL | FADE_FILLCOLOR_START | FADE_WHITETOBLACK
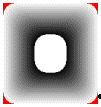
7) FADE_DUMPFILL | FADE_NOTRANSPARENCY
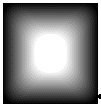
8) FADE_DUMPFILL | FADE_NOTRANSPARENCY | FADE_TRANSPARENCY_ DUMPCOLOR
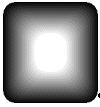
plus many other possibilities.
Second: using FADE_OUTER:
Region type:
rounded rectangle smaller than the above region, nInflate = 60
1) FADE_OUTER
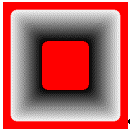
2) FADE_OUTER | FADE_WHITETOBLACK
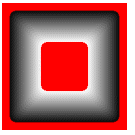
3) FADE_OUTER | FADE_DUMPFILL
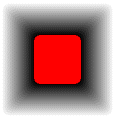
4) FADE_OUTER | FADE_DUMPFILL | FADE_WHITETOBLACK
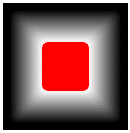
5) FADE_OUTER | FADE_DUMPFILL | FADE_WHITETOBLACK| FADE_NOTRANSPARENCY
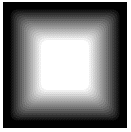
and so on………..