|
Available in LEADTOOLS Medical Imaging toolkits. |
#include "Ltdic.h"
pDICOMELEMENT LDicomDS::FindLastElement(pElement, nTag, bTree)
|
pDICOMELEMENT pElement; |
/* pointer to a DICOMELEMENT structure */ |
|
L_UINT32 nTag; |
/* tag that indicates the element to find */ |
|
L_BOOL bTree; |
/* flag that indicates how to evaluate the Data Set */ |
Returns a pointer to the last item in the Data Set with the specified tag.
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
|
pElement |
Pointer to a DICOMELEMENT structure within the Data Set. |
|
|
nTag |
Tag that specifies the item to find. For a list of default tag values, refer to Data Element Tag Constants. |
|
|
bTree |
Flag that indicates how the Data Set will be evaluated. Possible values are: |
|
|
|
Value |
Meaning |
|
|
TRUE |
Evaluate the Data Set as a tree. |
|
|
FALSE |
Evaluate the Data Set as a list. |
Returns
|
!NULL |
A pointer to a DICOMELEMENT structure that contains the last item in the Data Set with the specified tag. |
|
NULL |
An item with the specified tag was not found. |
Comments
If the Data Set is evaluated as a tree structure, this function returns the last item on the same level as pElement with the same parent as pElement, that has tag nTag.
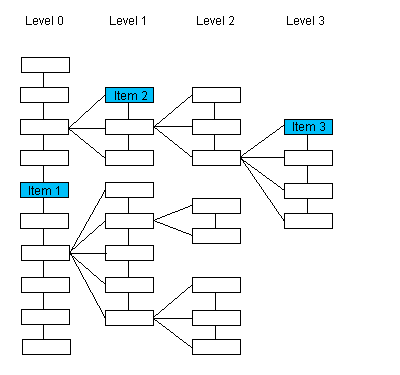
For the sake of these illustrations, the order of siblings is top to bottom. Therefore last is the item closest to the bottom.
Please note that the numbering of the items of interest in this first illustration is arbitrary and does not imply order.

|
If the passed pointer points to : |
The function returns a pointer to : |
|
Item 1 |
The last sibling (same level, same parent) of Item 1 that has tag nTag, if such an item exists. If such an item does not exist, the function returns NULL. Searching begins at the bottom. |
|
Item 2 |
The last sibling (same level, same parent) of Item 2 that has tag nTag, if such an item exists. If such an item does not exist, the function returns NULL. Searching begins at the bottom. |
|
Item 3 |
The last sibling (same level, same parent) of Item 3 that has tag nTag, if such an item exists. If such an item does not exist, the function returns NULL. Searching begins at the bottom. |
If the Data Set is evaluated as a list, this function returns the last item in the entire list that has tag nTag. Searching begins at the bottom of the list.
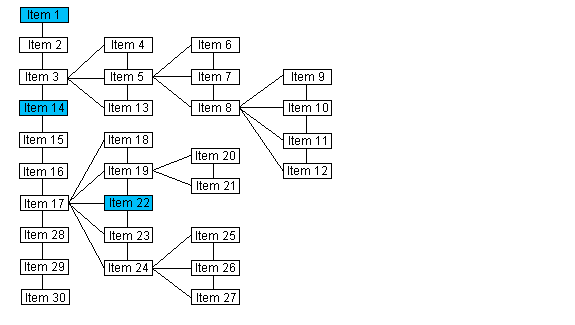
For the sake of these illustrations, the order of siblings is top to bottom. Therefore last is the item closest to the bottom.
Please note that the numbering of the items in this illustration does indicate the order of the items when the Data Set is evaluated as a list.
|
If the passed pointer points to : |
The function returns a pointer to : |
|
Item 1 |
The last item in the list that has tag nTag, if such an item exists. If an item with tag nTag is not found, NULL is returned. Searching begins at the bottom. |
|
Item 14 |
The last item in the list that has tag nTag, if such an item exists. If an item with tag nTag is not found, NULL is returned. Searching begins at the bottom. |
|
Item 22 |
The last item in the list that has tag nTag, if such an item exists. If an item with tag nTag is not found, NULL is returned. Searching begins at the bottom. |
The following functions will also help you find elements in the Data Set with a specific tag:
The following functions will help you find specific modules in the Data Set:
Required DLLs and Libraries
|
LTDIC For a listing of the exact DLLs and Libraries needed, based on the toolkit version, refer to Files To Be Included With Your Application |
Win32, x64
See Also
Example
This example displays in a list-box control the names of all elements.
L_INT LDicomDS_FindLastElementExample(CListBox *pDlg)
{
LDicomDS* pDS;
pDICOMELEMENT pElement;
pDICOMTAG pTag;
L_TCHAR szUnknown[]=TEXT("Unknown");
L_TCHAR* p;
pDS = new LDicomDS(NULL);
pDS->InitDS( CLASS_XA_BIPLANE_IMAGE_STORAGE_RETIRED, 0);
pElement = pDS->FindLastElement(NULL, TAG_SOP_CLASS_UID, FALSE);
if (pElement != NULL)
{
pTag = LDicomTag::Find(pElement->nTag);
if (pTag != NULL)
{
p = pTag->pszName;
}
else
{
p = szUnknown;
}
pDlg->AddString(p);
pElement = pDS->FindPrevElement(pElement, FALSE);
}
delete pDS;
return DICOM_SUCCESS;
}