|
Available in the LEADTOOLS Imaging toolkit. |
Flags for Setting a Region
By default, a bitmap does not have a region. You create a bitmap region by calling one or more of the SetRgn... methods. Each time you call one of these methods, you specify how the new region is to be added to the existing bitmap region (if there is one). The following is a list of the options:
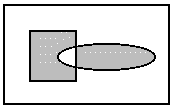
L_RGN_AND The resulting region includes only the
intersection of the existing region and the new one. The following example
shows the result, where the rectangles represent the existing region,
the ellipse represents the new one, and the shaded area represents the
resulting region.

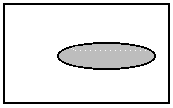
L_RGN_SET The resulting region includes only the
new region. The existing region, if any, is discarded. The following example
shows the result, where the ellipse is the new region and the shaded area
is the resulting region.
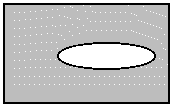
L_RGN_SETNOT The resulting region includes everything
in the bitmap, except the new region. The existing region, if any, is
discarded. The following example shows the result, where the ellipse is
the new region and the shaded area is the resulting region.
L_RGN_ANDNOTBITMAP The resulting region includes
the intersection of the area outside the existing region and the area
inside the new region. The following example shows the result, where the
rectangle is the existing region, the ellipse is the new one, and the
shaded area is the resulting region.
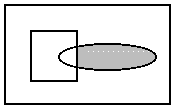
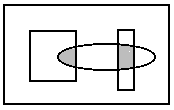
L_RGN_ANDNOTRGN The resulting region includes the
intersection of the area inside the existing region and the area outside
the new region. The following example shows the result, where the rectangle
is the existing region, the ellipse is the new one, and the shaded area
is the resulting region.
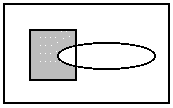
L_RGN_OR The resulting region includes the area
inside the existing region and the area inside the new region. The following
example shows the result, where the rectangle is the existing region,
the ellipse is the new one, and the shaded area is the resulting region.
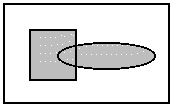
L_RGN_XOR The resulting region includes the area
inside the existing region and the area inside the new region, except
for any areas where the two intersect. The following example shows the
result, where the rectangle is the existing region, the ellipse is the
new one, and the shaded area is the resulting region.