LDicomDS::GetPrevElement
Summary
Returns a pointer to the item in the Data Set that immediately precedes the specified item.
Syntax
#include "Ltdic.h"
pDICOMELEMENT LDicomDS::GetPrevElement(pElement, bTree, bVolatile)
Parameters
pDICOMELEMENT pElement
Pointer to a DICOMELEMENTstructure that contains an item in the Data Set. A pointer to the item in the Data Set that immediately precedes this item will be returned.
L_BOOL bTree
Flag that indicates how the Data Set will be evaluated. Possible values are:
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| TRUE | Evaluate the Data Set as a tree. |
| FALSE | Evaluate the Data Set as a list. |
L_BOOL bVolatile
Flag that indicates the type of element to retrieve. Possible values are:
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| TRUE | Retrieve any previous element, volatile or non-volatile. |
| FALSE | Retrieve a non-volatile previous element. |
Returns
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| !NULL | A pointer to a DICOMELEMENTstructure that contains the item in the Data Set that immediately precedes the item specified in pElement. |
| NULL | There is not an item preceding pElement. (pElement is the first item in the Data Set.) |
Comments
If the Data Set is evaluated as a tree structure, this function returns the previous item on the same level as pElement with the same parent as pElement.
NOTE: The numbering of the items in this illustration is arbitrary and does not imply order.
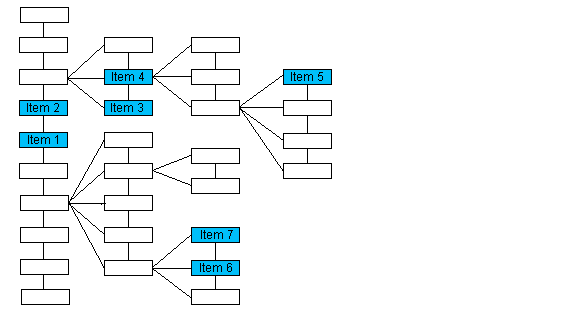
| If the passed pointer points to | The function returns a pointer to |
|---|---|
| Item 1 | Item 2 |
| Item 3 | Item 4 |
| Item 5 | NULL |
| Item 6 | Item 7 |
If the Data Set is evaluated as a list, the previous item in the list is returned.
NOTE: The numbering of the items in this illustration does indicate the order of the items when the Data Set is evaluated as a list.
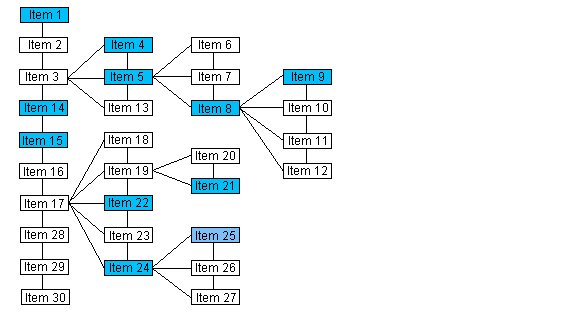
| If the passed pointer points to | The function returns a pointer to |
|---|---|
| Item 1 | NULL |
| Item 15 | Item 14 |
| Item 5 | Item 4 |
| Item 9 | Item 8 |
| Item 22 | Item 21 |
| Item 25 | Item 24 |
The following functions will also help you navigate the Data Set as either a tree or a list:
If you evaluate the Data Set as a tree, you can also use the following functions to navigate the tree:
A volatile element is an element that can be changed or destroyed in the process of inserting or setting an image. A non-volatile element is an element that must be changed manually. It is not changed or destroyed by inserting or setting an image.
For example, a grayscale image has elements TAG_SMALLEST_IMAGE_PIXEL_VALUE, TAG_LARGEST_IMAGE_PIXEL_VALUE, etc. If the image is changed to a color image, these elements disappear and the following elements appear: TAG_RED_PALETTE_COLOR_LOOKUP_TABLE_DESCRIPTOR, etc. These are volatile elements since they are changed or destroyed when an image is changed or set.
To retrieve a previous element that must be changed manually, i.e. is not volatile, set bVolatile to FALSE. To retrieve either volatile or non-volatile previous element, set bVolatile to TRUE.
Required DLLs and Libraries
- LTDIC
- For a listing of the exact DLLs and Libraries needed, based on the toolkit version, refer to Files To Be Included With Your Application
Platforms
Win32, x64
See Also
Functions
- LDicomDS::GetFirstElement
- [LDicomDS:GetPrevElement
- LDicomDS::GetNextElement
- LDicomDS::GetCountModule
- LDicomDS::GetRootElement
- LDicomDS::GetParentElement
- LDicomDS::GetChildElement
- LDicomDS::IsVolatileElement
Topics
Example
This example displays in a list-box control all elements (level 0) from the Data Set.
L_INT LDicomDS_GetPrevElementExample(CListBox *pDlg){LDicomDS* pDS;pDICOMELEMENT pElement;pDICOMTAG pTag;L_TCHAR szUnknown[]=TEXT("Unknown");L_TCHAR* p;pDS = new LDicomDS(NULL);pDS->InitDS( CLASS_XA_BIPLANE_IMAGE_STORAGE_RETIRED, 0);pElement = pDS->GetLastElement(NULL, TRUE, FALSE);while (pElement != NULL){pTag = LDicomTag::Find(pElement->nTag);if (pTag != NULL){p = pTag->pszName;}else{p = szUnknown;}pDlg->AddString(p);pElement = pDS->GetPrevElement(pElement, TRUE, FALSE);}delete pDS;return DICOM_SUCCESS;}
© 1991-2023 LEAD Technologies, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
