L_DicomGetPrevElement
Summary
Returns a pointer to the item in the Data Set that immediately precedes the specified item.
Syntax
#include "Ltdic.h"
L_LTDIC_API pDICOMELEMENT L_DicomGetPrevElement(hDS, pElement, bTree, bVolatile)
Parameters
HDICOMDS hDS
A DICOM handle.
pDICOMELEMENT pElement
Pointer to a DICOMELEMENTstructure that contains an item in the Data Set. A pointer to the item in the Data Set that immediately precedes this item will be returned.
L_BOOL bTree
Flag that indicates how the Data Set will be evaluated. Possible values are:
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| TRUE | Evaluate the Data Set as a tree. |
| FALSE | Evaluate the Data Set as a list. |
L_BOOL bVolatile
Flag that indicates the type of element to retrieve. Possible values are:
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| TRUE | Retrieve any previous element, volatile or non-volatile. |
| FALSE | Retrieve a non-volatile previous element. |
Returns
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| !NULL | A pointer to a DICOMELEMENTstructure that contains the item in the Data Set that immediately precedes the item specified in pElement. |
| NULL | There is not an item preceding pElement. (pElement is the first item in the Data Set.) |
Comments
If the Data Set is evaluated as a tree structure, this function returns the previous item on the same level as pElement with the same parent as pElement. Please note that the numbering of the items in this illustration is arbitrary and does not imply order.
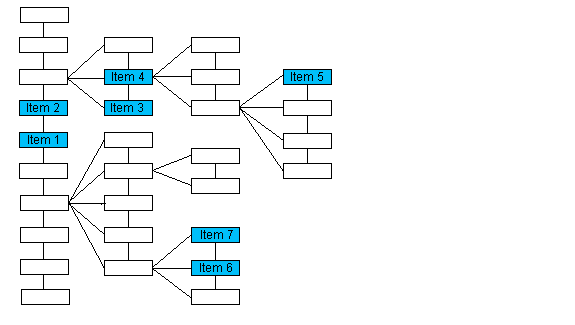
| If the passed pointer points to | The function returns a pointer to |
|---|---|
| Item 1 | Item 2 |
| Item 3 | Item 4 |
| Item 5 | NULL |
| Item 6 | Item 7 |
If the Data Set is evaluated as a list, the previous item in the list is returned. Please note that the numbering of the items in this illustration does indicate the order of the items when the Data Set is evaluated as a list.
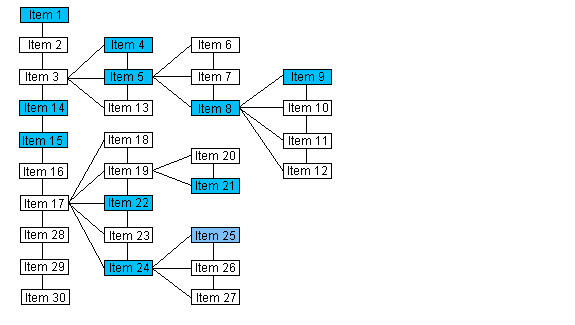
| If the passed pointer points to | The function returns a pointer to |
|---|---|
| Item 1 | NULL |
| Item 15 | Item 14 |
| Item 5 | Item 4 |
| Item 9 | Item 8 |
| Item 22 | Item 21 |
| Item 25 | Item 24 |
The following functions will also help you navigate the Data Set as either a tree or a list:
If you evaluate the Data Set as a tree, you can also use the following functions to navigate the tree:
A volatile element is an element that can be changed or destroyed in the process of inserting or setting an image. A non-volatile element is an element that must be changed manually. It is not changed or destroyed by inserting or setting an image.
For example, a grayscale image has elements TAG_SMALLEST_IMAGE_PIXEL_VALUE, TAG_LARGEST_IMAGE_PIXEL_VALUE, etc. If the image is changed to a color image, these elements disappear and the following elements appear: TAG_RED_PALETTE_COLOR_LOOKUP_TABLE_DESCRIPTOR, etc. These are volatile elements since they are changed or destroyed when an image is changed or set.
To retrieve a previous element that must be changed manually, i.e. is not volatile, set bVolatile to FALSE. To retrieve either volatile or non-volatile previous element, set bVolatile to TRUE.
Required DLLs and Libraries
- LTDIC
- For a listing of the exact DLLs and Libraries needed, based on the toolkit version, refer to Files To Be Included With Your Application
Platforms
Win32, x64, Linux.
See Also
Functions
- L_DicomGetFirstElement
- L_DicomGetPrevElement
- L_DicomGetNextElement
- L_DicomGetCountModule
- L_DicomGetRootElement
- L_DicomGetParentElement
- L_DicomGetChildElement
- L_DicomIsVolatileElement
Topics
Example
This example displays in a list-box control all elements (level 0) from the Data Set
L_INT DicomGetPrevElementExample(HWND hDlg){HDICOMDS hDS;pDICOMELEMENT pElement;pDICOMTAG pTag;L_TCHAR szUnknown[]=TEXT("Unknown");L_TCHAR *p;hDS = L_DicomCreateDS(NULL);L_DicomInitDS(hDS, CLASS_XA_BIPLANE_IMAGE_STORAGE_RETIRED, 0);pElement = L_DicomGetLastElement(hDS, NULL, TRUE, FALSE);while (pElement != NULL){pTag = L_DicomFindTag(pElement->nTag);if (pTag != NULL){p = pTag->pszName;}else{p = szUnknown;}SendMessage(hDlg, LB_ADDSTRING, (WPARAM)0, (LPARAM)(LPCTSTR)p);pElement = L_DicomGetPrevElement(hDS, pElement, TRUE, FALSE);}L_DicomFreeDS(hDS);return DICOM_SUCCESS;}
© 1991-2023 Apryse Sofware Corp. All Rights Reserved.
