Add References and Set a License - macOS Swift App
This tutorial shows how to create a project, add references, and set the license in a Swift macOS App application using the LEADTOOLS SDK.
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Summary | This tutorial covers how to set your LEADTOOLS license in a Swift macOS App application. |
| Completion Time | 20 minutes |
| Project | Download tutorial project (14 KB) |
| Platform | Swift macOS App Application |
| IDE | Xcode |
| Runtime License | Download LEADTOOLS |
| Try it in another language |
|
Required Knowledge
Before any functionality from the SDK can be leveraged, a valid runtime license will have to be set.
For instructions on how to obtain a runtime license refer to Obtaining a License.
Create the Project
Launch Xcode and select Create a new Xcode project.

Next, select macOS at the top and App under the Application section, then click Next.
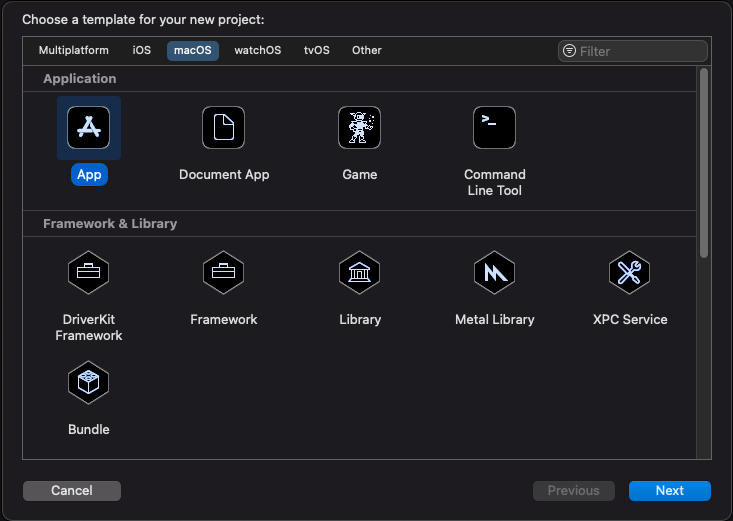
In the next section, fill in the following and click Next:
- Product Name (This is the name of your application)
- Team (This is from the Apple Developer Program)
- Organization Info (Typically an inverse of your organization web address, IE: com.leadtools for leadtools.com)
- Language (This tutorial is written in Swift)
Note: The
Organization IdentifierandProduct Namecombine to make theBundle Identifier, which must be unique.Important Note: For this tutorial ensure
Interfaceis set to Storyboard.
Lastly, select the location to save the new project to and click Create.
Add the LEADTOOLS Framework Packages
To leverage the LEADTOOLS SDK in a Swift macOS App project, references to the LEADTOOLS Framework files will be needed.
Framework files can be added by one of the following two methods:
- Clicking and dragging them to the
Frameworks and Librariessection - Clicking the
+icon at the bottom of theFramework and Librariessection, then selectingAdd Filesfrom theAdd Otherdrop down.
The LEADTOOLS Frameworks can be found here: <INSTALL_DIR>/LEADTOOLS23/Bin/Xcode/Frameworks/macOS
Once a framework file is added, a new folder called Frameworks will be added to the Project Navigator, containing the added framework files.
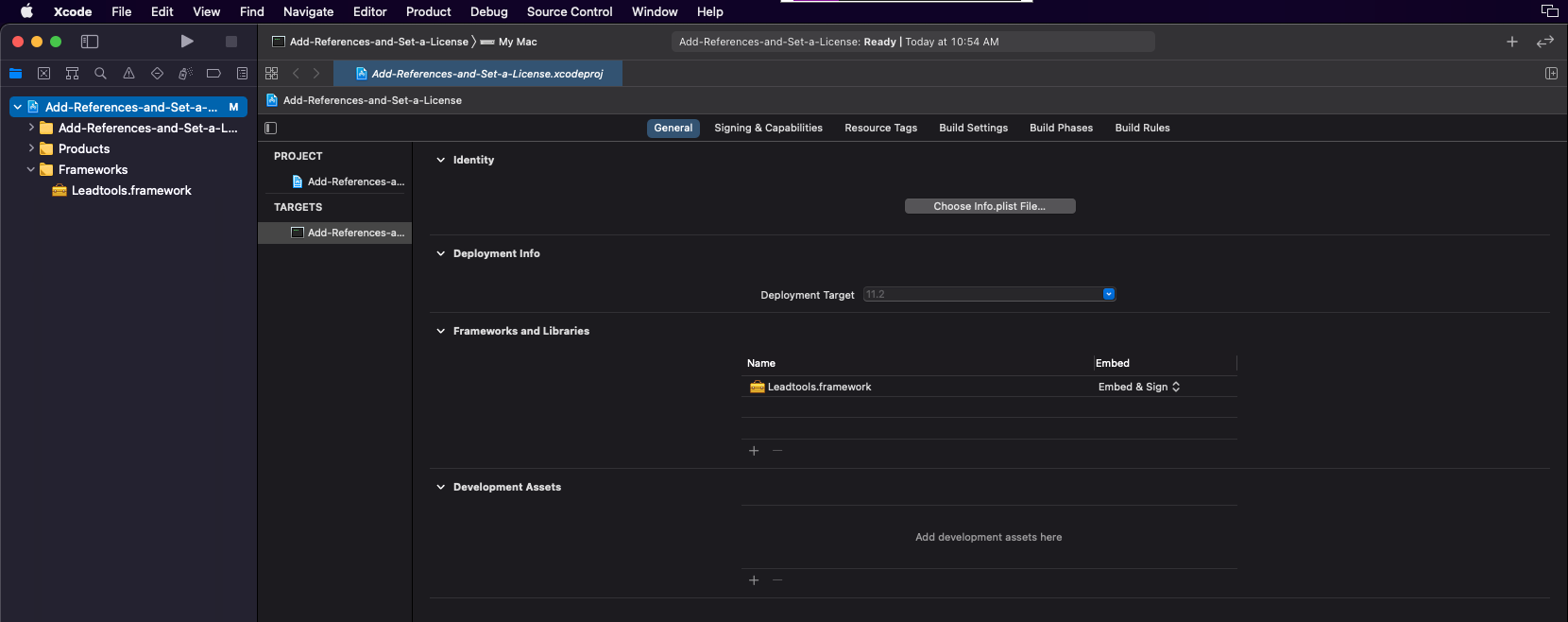
To allow Xcode to utilize these Framework files, a few more steps are required.
-
First click on Build Settings and in the
Searchfield typeHeader. This will help reduce the number of entries and make it easier to find the two sections we need to adjust. -
Scroll to the bottom and under the Search Paths section, find the entry
Framework Search Path. Double-click to the right of it, where the other sections have Yes/No values listed, to bring up a screen allowing you to add values. From there click on+and type in the path to the framework files given above. When complete select the up-down arrows next tonon-recursiveand switch it torecursive.
If done correctly the entry should look something like this:
Framework Search Paths <INSTALL_DIR>/LEADTOOLS23/Bin/Xcode/Frameworks/macOS/**
Next, find the entry called Objective-C Bridging Header, under the Swift Compiler - General section. Also, double-click to the right of it and type in the following and hit entry:
-
Leadtools-Bridging-Header.h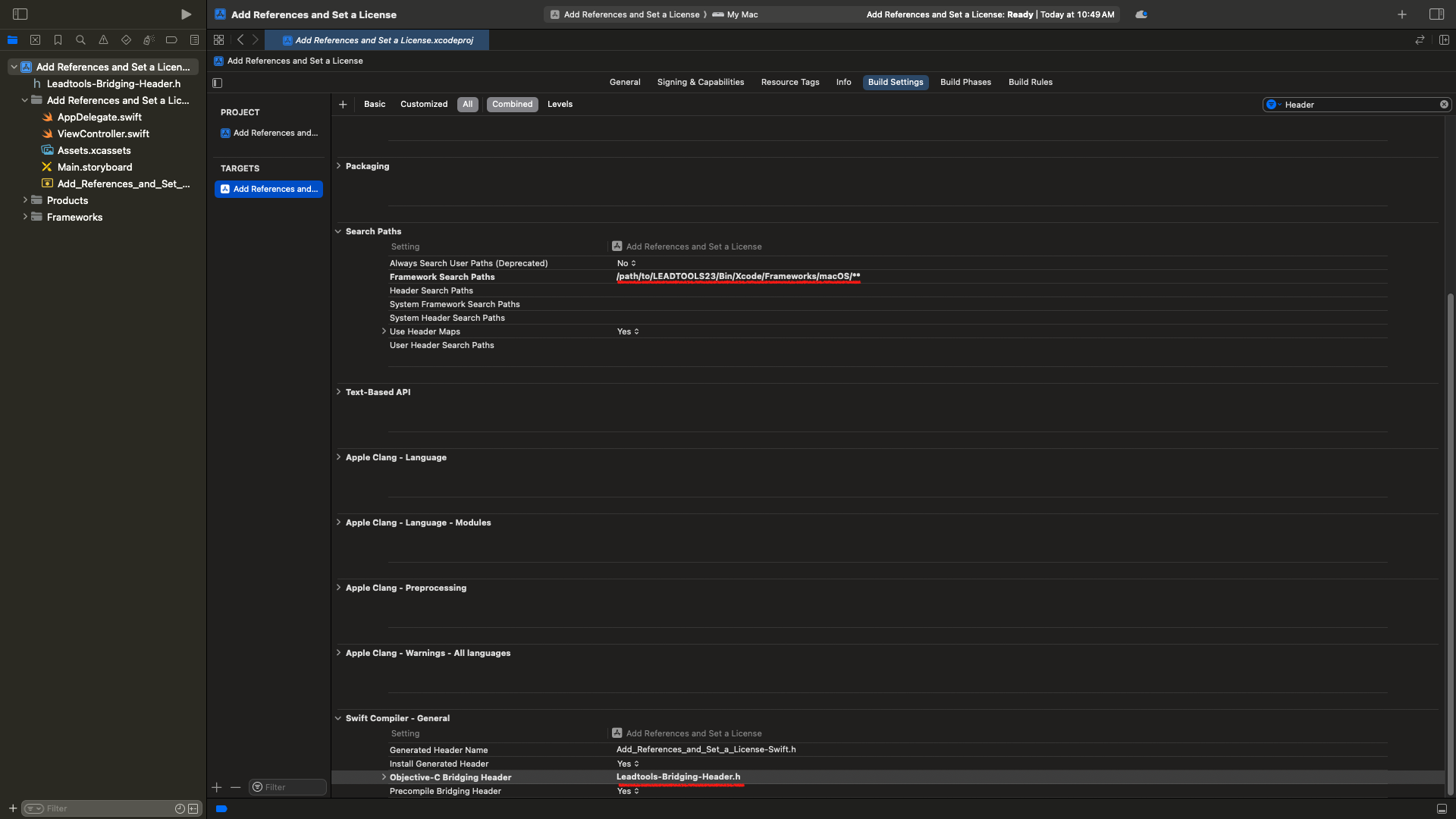
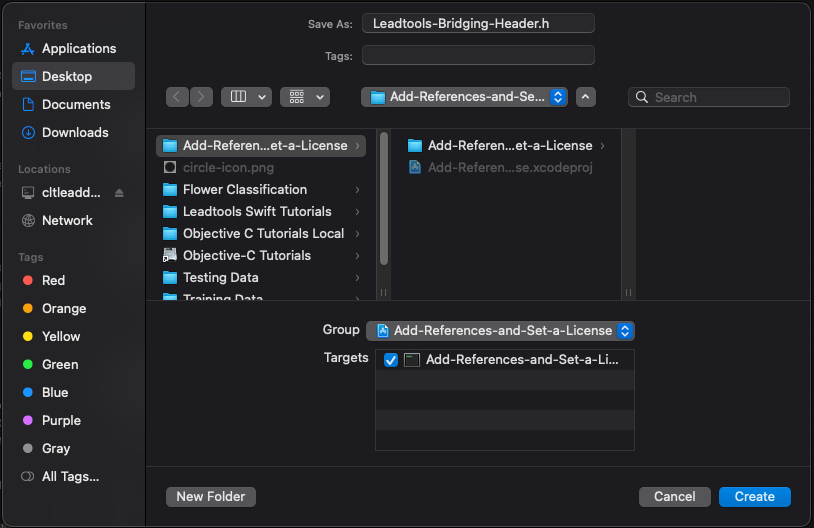
Right-click on the blue file in the Project Manager and select New File.... In the new window select Header File from the macOS and Source sections and click Next. At the top change the Save As: name to Leadtools-Bridging-Header.h, which is the same name as the one provided in the Objective-C Bridging Header entry above and MUST match. Then click the check box under the Targets section, as shown in the screenshot below, and click Create.
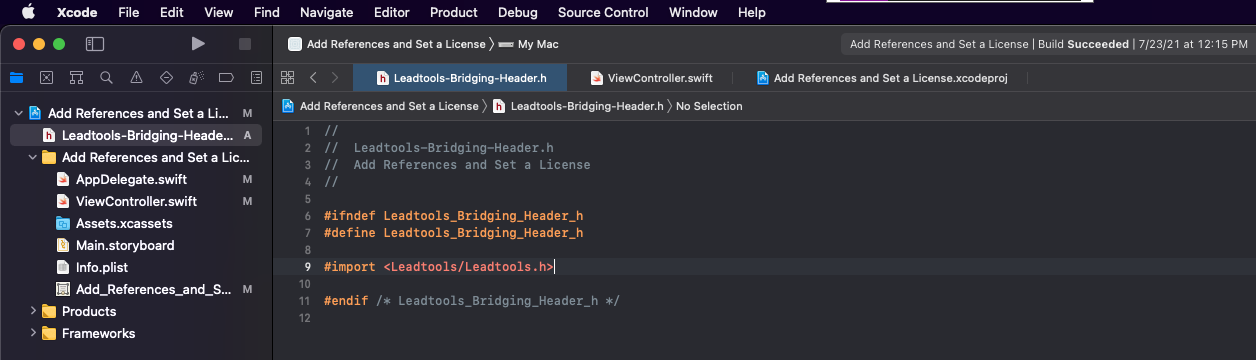
The new .h file will be displayed upon creation. Between the #define and #endif section, list the framework .h files containing the API needed for the project.
For the purposes of this tutorial, only the main leadtools.h file is needed, so list it as follows:
#import <Leadtools/Leadtools.h> Note
All framework imports will follow the same structure, IE: for leadtools.codecs it would be
#import <Leadtools.Codecs/Leadtools.Codecs.h>.
Once finished click Project -> Build, or Command B, to build the project. If done correctly everything should build without error, if you have any errors double check the paths and file names provided in the prior sections.
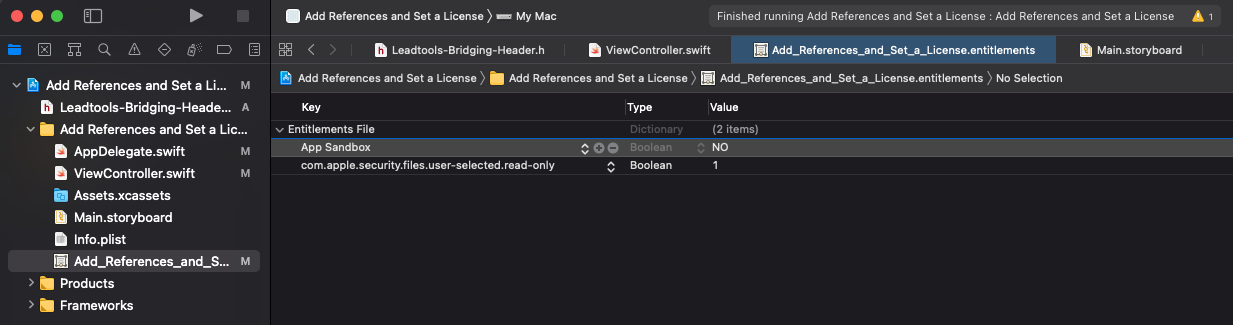
Given this is a macOS App project, it is by default sandboxed and not allowed to access files outside of the Documents folder. Since we need to access the license file in the LEADTOOLS folder we need to remove the sandbox limitation. To do so, open Add_References_and_Set_a_License.entitlements and set App Sandbox to NO.
Add the Set License Code
With the project created and the frameworks installed, coding can begin.
Open the ViewController.swift file. Below the existing viewDidLoad() and represendedObject sections, create a new override func called viewDidAppear(). Like the above viewDidLoad(), these are different states in the app loading process. Within this function call SetLicense() in order to properly display license status messages in the App UI.
override func viewDidLoad() {super.viewDidLoad()// Do any additional setup after loading the view.}override var representedObject: Any? {didSet {// Update the view, if already loaded.}}override func viewDidAppear() {SetLicense()}
Next, create a new standard func called showAlert(message: String, title: String). This function is called from the SetLicense function and is responsible for displaying pop-up style messages in the App UI.
func showAlert(message: String, title: String) {let alert = NSAlert()alert.messageText = titlealert.informativeText = messagealert.addButton(withTitle: "OK")alert.alertStyle = .warningif let window = view.window ?? NSApplication.shared.windows.first {alert.beginSheetModal(for: window) { modalResponse inif modalResponse == .alertFirstButtonReturn {print("Alert Dismissed")}}}}
Finally, create a new func called SetLicense() and call it inside the viewDidAppear function, as shown above. Add the following code to properly set your LEADTOOLS license.
func SetLicense() {let license = "/path/to/LEADTOOLS23/Support/Common/License/Leadtools.lic"let keyFile = String("\(license).key")do {let key = try String(contentsOfFile: keyFile)try LTRasterSupport.setLicense(file: license, developerKey: key)} catch {print("Unable to read contents of .key file.\n\(error.localizedDescription)")}if LTRasterSupport.kernelExpired {showAlert(message: "License file invalid or expired.", title: "Leadtools License")print("License file invalid or expired.")} else {showAlert(message: "License file set successfully!", title: "Leadtools License")print("License file set successfully!")}}
Run the Project
Clean the project to clear any errors by selecting Product -> Clean Build Folder or Shift + Command + K.
Run the project by selecting Product -> Run or Command + R.
If the steps were followed correctly, the app will launch and a message will display in the Output window stating License file set successfully
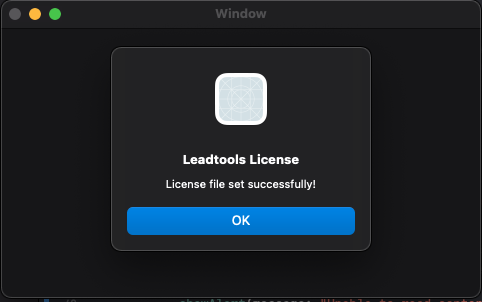
Wrap-up
This tutorial showed how to create a new Swift macOS App project, add LEADTOOLS Frameworks and Header files, and set the license.
This is the basis for all Swift macOS App applications leveraging the LEADTOOLS SDK. All functionality in the SDK is unlocked via setting a license. The setLicense() function must be called before calling any other LEADTOOLS SDK functions.
Once the SDK is purchased, the evaluation license can be replaced with a valid runtime license to disable the Nag Message.
