Add Transparency to an Image - Windows C DLL
This tutorial shows how to create and save a transparent area in an image applying two different techniques in a Windows C/C++ API application using the LEADTOOLS SDK.
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Summary | This tutorial covers how to add transparency to images in a Windows C DLL application. |
| Completion Time | 30 minutes |
| Visual Studio Project | Download tutorial project (18 KB) |
| Platform | Windows C DLL Application |
| IDE | Visual Studio 2017, 2019, 2022 |
| Development License | Download LEADTOOLS |
| Try it in another language |
|
Required Knowledge
Get familiar with the basic steps of creating a project and loading/displaying an image by reviewing the Add References and Set a License and Load, Display, and Save Images tutorials, before working on the Add Transparency to an Image - Windows C DLL tutorial.
Create the Project and Add LEADTOOLS References
Start with a copy of the project created in the Add References and Set a License tutorial. If the project is not available, create it by following the steps in that tutorial.
Open the pre-compiled header file (either pch.h or stdafx.h, depending on the version of Visual Studio used) and ensure the below lines are added.
#define LTV23_CONFIG#include "C:\LEADTOOLS23\Include\L_Bitmap.h" // use the actual path where LEADTOOLS is installed#pragma comment (lib, "C:\\LEADTOOLS23\\Lib\\CDLL\\x64\\Ltkrn_x.lib")#pragma comment (lib, "C:\\LEADTOOLS23\\Lib\\CDLL\\x64\\Ltdis_x.lib") // needed for region processing#pragma comment (lib, "C:\\LEADTOOLS23\\Lib\\CDLL\\x64\\Ltfil_x.lib") // file loading and saving
Note: For a complete list of DLLs that are required for specific application features, refer to Files to be Included with your Application - C API
Set the License File
The License unlocks the features needed for the project. It must be set before any toolkit functionality is called. For details, including tutorials for different platforms, refer to Setting a Runtime License.
There are two types of runtime licenses:
- Evaluation license, obtained at the time the evaluation toolkit is downloaded. It allows the toolkit to be evaluated.
- Deployment license. If a Deployment license file and developer key are needed, refer to Obtaining a License.
Note: Adding LEADTOOLS references and setting a license are covered in more detail in the Add References and Set a License tutorial.
Add the Code to Create Alpha Channel Transparency
With the project created, the references added, the license set, and the load image code added, coding can begin.
Open the project's CPP file and add a new function called AddAlphaTransparency() that takes an image and sets all white and near-white areas in it as transparent by manipulating the image's alpha channel. Place this function above the WndProc() function.
// modify the input bitmap by adding an alpha channel with transparent white areasvoid AddAlphaTransparency(BITMAPHANDLE *pBitmap){// createa an 8-bit image to use later as Alpha channelBITMAPHANDLE alpha = { 0 };L_CreateBitmap(&alpha, sizeof BITMAPHANDLE, TYPE_CONV, BITMAPWIDTH(pBitmap), BITMAPHEIGHT(pBitmap),0, // zero siginfies 8-bit grayscaleORDER_RGB, NULL, pBitmap->ViewPerspective, NULL, NULL);L_COLORREF colorNearWhite = RGB(245, 245, 245), colorWhite = RGB(255, 255, 255);// Fill the alpha channel with white to cause all pixels to be opaqueL_FillBitmap(&alpha, colorWhite);// find pixels from near-white to white in the input image and create region from themL_SetBitmapRgnColorRGBRange(pBitmap, colorNearWhite, colorWhite, L_RGN_SET);// copy the region to the alpha imageL_HRGN hRgn = NULL;L_GetBitmapRgnHandle(pBitmap, NULL, &hRgn);L_SetBitmapRgnHandle(&alpha, NULL, hRgn, L_RGN_SET);// fill the region with black to represent transparent pixels.L_FillBitmap(&alpha, RGB(0, 0, 0));DeleteObject(hRgn);L_FreeBitmapRgn(pBitmap);L_FreeBitmapRgn(&alpha);// Re-insert the modified 8-bit image as the main image's alpha channelL_SetBitmapAlpha(pBitmap, &alpha);L_FreeBitmap(&alpha);}
Add the Code to Set a Specific Color as Transparent
Add a new function called AddTransparentColor() that takes an image and converts all white and near-white areas to pure white, then marks the white color as transparent. Place this function above the WndProc() function.
void AddTransparentColor(BITMAPHANDLE *pBitmap){// find pixels from near-white to white in the input image and create region from themL_COLORREF colorNearWhite = RGB(245, 245, 245), colorWhite = RGB(255, 255, 255);L_SetBitmapRgnColorRGBRange(pBitmap, colorNearWhite, colorWhite, L_RGN_SET);// Fill the region with a single white color to enable setting it as a unique transparent colorL_FillBitmap(pBitmap, colorWhite);L_FreeBitmapRgn(pBitmap);pBitmap->Flags.Transparency = true;pBitmap->Transparency = colorWhite;}
Add the Code to Load an Image and Save it With Transparency
In the Solution Explorer, double-click the resources file (.rc).
Add a new &Add Transparency menu item to the File drop-down menu and move it above the Exit and Save items. Leave the new menu item's ID as ID_FILE_ADDTRANSPARENCY.
Load a base image to have transparency added to it and pass it to the 2 methods created above:
- Pass the base image to
AddAlphaTransparency()then save the resulting image as 32-bit PNG to store the transparency alpha channel with it. - Pass the base image to
AddTransparentColor()then save the resulting image either as PNG or GIF, since both formats support transparent color.
Open the project's CPP file and navigate to the WndProc function. Under the switch (wmId) statement that is below the WM_COMMAND case, add a new case and the code below.
switch (wmId){case ID_FILE_ADDTRANSPARENCY:{BITMAPHANDLE bmp = { 0 };L_LoadBitmap((L_TCHAR*)TEXT("C:\\LEADTOOLS23\\Resources\\Images\\testframe1.jpg"), &bmp, sizeof BITMAPHANDLE, 24, ORDER_BGR, NULL, NULL);AddAlphaTransparency(&bmp); // create alpha channel with transparent parts corresponding to all near-white parts// Save as 32-bit PNG to include alpha in output imageL_SaveBitmap((L_TCHAR*)TEXT("C:\\LEADTOOLS23\\Resources\\Images\\imagePlusAlpha.png"), &bmp, FILE_PNG, 32, 9, NULL);AddTransparentColor(&bmp); // make all near-white parts a single color and mark it as transparent// Save as 8-bit GIF which supports transparent color, but not Alpha channel.L_SaveBitmap((L_TCHAR*)TEXT("C:\\LEADTOOLS23\\Resources\\Images\\imageWithTranspColor.gif"), &bmp, FILE_GIF, 8, 0, NULL);L_FreeBitmap(&bmp);}break;// Keep rest of the code as is
Run the Project
Run the project by pressing F5, or by selecting Debug -> Start Debugging.
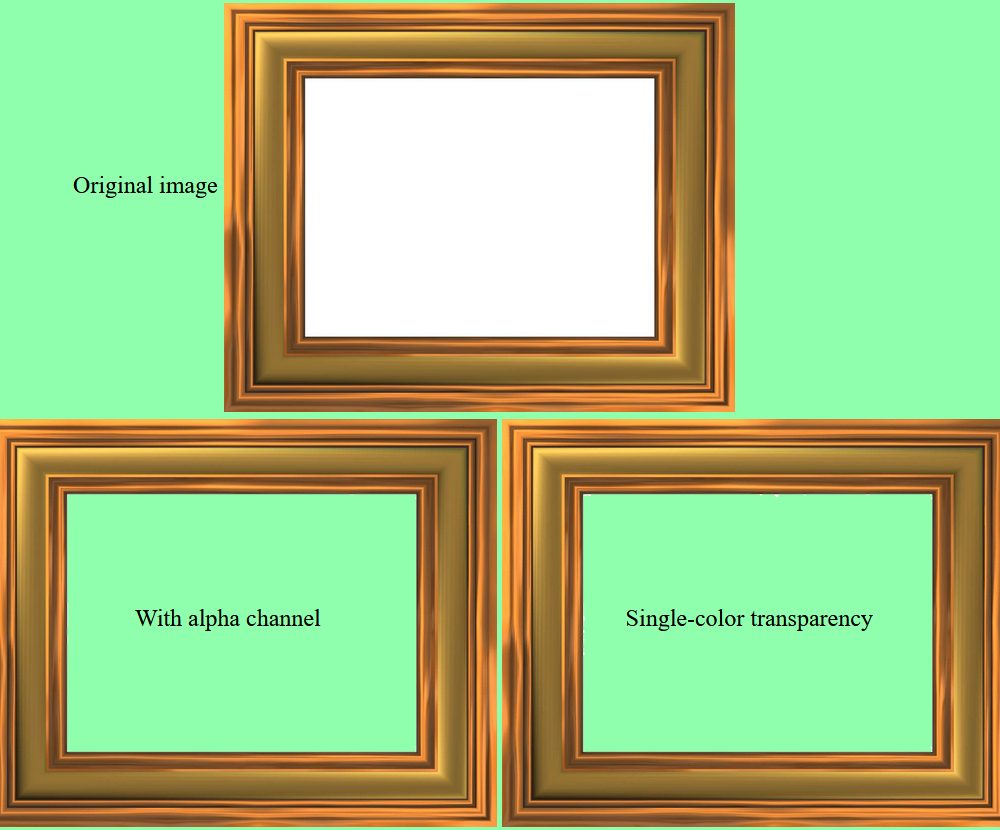
If the steps are followed correctly, the application runs and loads a JPEG image, adds transparency to it in two different ways and saves the resulting images with transparency to two different files.
This image can be used for input. The screenshot below shows how the input image is displayed along with the two resulting images that contain trasparency information when all three images are placed in a web page that has color background.
Wrap-up
This tutorial showed how to use the various LEADTOOLS functions to load, process and save an image to add transparency information to bitmaps.
