Convert Documents Using AWS Lambda - C# .NET 6
This tutorial shows how to set up Amazon Web Services (AWS) Lambda for use with the LEADTOOLS SDK and convert a document with .NET.
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Summary | This tutorial covers how to set up Amazon Web Services (AWS) Lambda for use with the LEADTOOLS SDK and convert a document with .NET. |
| Completion Time | 60 minutes |
| Visual Studio Project | Download tutorial project (35 MB) |
| Platform | AWS Lambda .NET Application |
| IDE | Visual Studio 2022, AWS Lambda Visual Studio Extension |
| Development License | Download LEADTOOLS |
Required Knowledge
Get familiar with the basic steps of creating a project by reviewing the Add References and Set a License tutorial, before working on the Convert Documents Using AWS Lambda - C# .NET 6 tutorial.
Complete the AWS Setup for Visual Studio
To set up the development environment to use AWS in Visual studio, complete the following 2 tutorials from Amazon:
- Using the AWS Lambda Templates in the AWS Toolkit for Visual Studio
- Using the AWS Lambda Project in the AWS Toolkit for Visual Studio
After these tutorials are completed, the AWS Toolkit for Visual Studio should be installed and a basic understanding of how to create a new AWS Lambda Project for .NET and publish to AWS should be acquired.
Create an Empty Function
In Visual Studio, create a new AWS Lambda Project (.NET - C#) Project. Give the project a name and location and click Create.
Select an Empty Function and click OK.
Add LEADTOOLS References
The references needed depend upon the purpose of the project. For this project, the following DLL's is needed:
Leadtools.dllLeadtools.Codecs.dllLeadtools.Core.dllLeadtools.Document.Converter.dllLeadtools.Document.Pdf.dllLeadtools.Document.Raster.dllLeadtools.Document.Writer.dllLeadtools.Document.dllLeadtools.Ocr.LEADEngine.dllLeadtools.Ocr.dll
For a complete list of which Codec DLLs are required for specific formats, refer to File Format Support.
Add the LEADRequest.cs Class
Right-click the C# project and select Add, then Class. Name it LEADRequest.cs and click Add. This class will be used as a structure for the Lambda requests to follow.
Copy the code below to add the needed functionality to the class:
public class LEADRequest{public string InputUrl { get; set; }public DocumentFormat DocumentFormat { get; set; }}
Add the LEADLambdaHandler Class
Right-click the C# project and select Add, then Class. Name it LEADLambdaHandler.cs and click Add.
In the new class, add the following to the using block:
using Leadtools.Document.Converter;using Leadtools.Document.Writer;using Leadtools.Document;using Leadtools;using Leadtools.Ocr;using System.Diagnostics;
Copy the code below to add the needed functionality to the class:
public class LEADLambdaHandler{// Global VariablesIOcrEngine ocrEngine;DocumentConverter documentConverter;static HttpClient httpClient = new();// Constructor which handles all initialization to make sure the function is as fast as possible once it is warmed uppublic LEADLambdaHandler(){InitEnvironment();Platform.LibraryPath = "/opt/native-runtimes/";InitLEADTOOLS();}// Method which initializes the Lambda environment for use by the LEADTOOLS SDKvoid InitEnvironment(){// Set the LD_LIBRARY_PATH in function console to include:// /var/lang/lib:/lib64:/usr/lib64:/var/runtime:/var/runtime/lib:/var/task:/var/task/lib:/opt/lib:/tmpExecuteBashCommand("ln -s /lib64/libdl.so.2 /tmp/libdl.so");}// Initialize the LEADTOOLS SDK Classesvoid InitLEADTOOLS(){SetLicense();RasterDefaults.TemporaryDirectory = "/tmp";RasterDefaults.SetResourceDirectory(LEADResourceDirectory.Fonts, "/opt/ShadowFonts");ocrEngine = OcrEngineManager.CreateEngine(OcrEngineType.LEAD);ocrEngine.Startup(null, null, "/tmp", "/opt/OcrLEADRuntime");documentConverter = new DocumentConverter();documentConverter.SetOcrEngineInstance(ocrEngine, true);}// Helper method for executing shell scripts in the Lambda environmentstring ExecuteBashCommand(string command){command = command.Replace("\"", "\"\"");var proc = new Process{StartInfo = new ProcessStartInfo{FileName = "/bin/bash",Arguments = "-c \"" + command + "\"",UseShellExecute = false,RedirectStandardOutput = true,CreateNoWindow = true}};proc.Start();proc.WaitForExit();return proc.StandardOutput.ReadToEnd();}// Set license code TODO: Replace the licString and developerKey with a valid license and keyvoid SetLicense(){string licString = "[License]\n" + "License = <doc><ver>2.0</ver>`ADD LICENSE HERE`</doc>";string developerKey = "ADD DEVELOPMENT KEY HERE";byte[] licBytes = System.Text.Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(licString);RasterSupport.SetLicense(licBytes, developerKey);}// Main conversion functionpublic string ConvertDocument(LEADRequest request, StringWriter sw){var isUrl = Uri.IsWellFormedUriString(request.InputUrl, UriKind.RelativeOrAbsolute);if (isUrl){var response = httpClient.GetAsync(request.InputUrl).Result;if (response.IsSuccessStatusCode){var stream = response.Content.ReadAsStreamAsync().Result;using var document = DocumentFactory.LoadFromStream(stream, new LoadDocumentOptions());string ext = DocumentWriter.GetFormatFileExtension(request.DocumentFormat);string fileName = Path.Combine("/tmp", Path.ChangeExtension(Path.GetFileName(request.InputUrl), ext));DocumentConverterJobData jobData = DocumentConverterJobs.CreateJobData(document, fileName, request.DocumentFormat);DocumentConverterJob job = documentConverter.Jobs.CreateJob(jobData);documentConverter.Jobs.RunJob(job);if (job.Errors.Count > 0)foreach (var error in job.Errors)sw.WriteLine($"Error during conversion: {error.Error.Message} {error.Error.StackTrace}");// This code reads the text from the newly created PDF to ensure the conversion was successfulusing LEADDocument doc = DocumentFactory.LoadFromFile(fileName, new LoadDocumentOptions());doc.Text.OcrEngine = ocrEngine;foreach (DocumentPage page in doc.Pages){DocumentPageText page_text = page.GetText();page_text.BuildText();string _text = page_text.Text;sw.WriteLine($"Page Number: {page.PageNumber}\n");sw.WriteLine($"{_text}\n");}return fileName;}elsesw.WriteLine("Download of URL is not successful");}elsesw.WriteLine("Url is invalid.");return null;}}
Set the License File
The License unlocks the features needed for the project. It must be set before any toolkit function is called. For details, including tutorials for different platforms, refer to Setting a Runtime License.
There are two types of runtime licenses:
- Evaluation license, obtained at the time the evaluation toolkit is downloaded. It allows the toolkit to be evaluated.
- Deployment license. If a Deployment license file and developer key are needed, refer to Obtaining a License.
Note: Adding LEADTOOLS NuGet and local references and setting a license are covered in more detail in the Add References and Set a License tutorial.
Update the FunctionHandler
When an AWS Lambda function is triggered, the FunctionHandler method is called. Everything in the Function class that is global will be called before that when the function is first starting up. While the container is warm, it will only call the FunctionHandler method until the execution context changes.
In order to leverage this functionality, most of the initialization code for the LEADLambdaHandler is done in the constructor to keep each function call as fast as possible while the container is warm.
Open the Function.cs file that was included as part of the project and add the following to the using block under the rest of the using statements.
using Amazon.Lambda.Core; Add the following global variable to the Function class:
public LEADLambdaHandler LEADHandler = new LEADLambdaHandler(); Replace the FunctionHandler method with the one below to accept a LEADRequest as the input instead of a string input, and then call the LEADHandler.ReadBarcode method:
public string FunctionHandler(LEADRequest request, ILambdaContext context){StringWriter sw = new();try{string outputFile = LEADHandler.ConvertDocument(request, sw);if (outputFile != null)sw.WriteLine($"Successfully saved to {outputFile}.");elsesw.WriteLine("Error occurred. Output file not saved.");}catch (Exception ex){sw.WriteLine(ex.Message);sw.WriteLine(ex.StackTrace);if (ex.InnerException != null){sw.WriteLine(ex.InnerException.Message);sw.WriteLine(ex.InnerException.StackTrace);}}return sw.ToString();}
Once all the code is added, build the project to ensure everything is working as intended.
Gather the Required Lambda Dependencies
Note: This step can be skipped if desired. The
lead-deps-layer.zipis already included with this project's download.
The LEADTOOLS SDK requires certain dependencies to be installed on a Linux machine in order to function properly. For a full list, see Files to be Included with your Linux Application.
Create the Lambda Layer
The LEADTOOLS SDK requires runtime dependencies to be installed in the Lambda function. In order to keep packages small and flexible, Lambda Layers are used. For more information on what a Layer is, refer to AWS Lambda Layers.
- Create a new folder named
lead-deps-layer - Create two new sub folders within this folder called
native-runtimesandOcrLEADRuntime - Copy all necessary dependency files from
<INSTALL_DIR>/LEADTOOLS23/Bin/Linux/x64folder to thenative-runtimesfolder - Copy all necessary dictionary files form
<INSTALL_DIR>/LEADTOOLS23/Bin/Common/OcrLEADRuntimefolder to the newOcrLEADRuntime -
Zip all files within the folder, ensure there is not a folder within the zip file. View the screenshot below for reference.
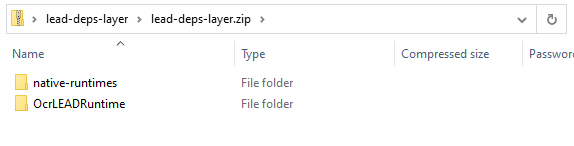
Upload the Layer Zip File
Once the layer zip is created, it needs to be uploaded to AWS Lambda.
- Navigate to the AWS Lambda Console and sign in
- On the left-hand panel, select Layers
- In the main window, select Create Layer
- Name the layer
lead-deps-layer - Give it a description
- Click Upload and choose the
lead-deps-layer.zip - In the Runtimes dropdown, select .NET 6 (C#/PowerShell)
- Click Create to create the layer
Publish Lambda Function to AWS
Once the layer is completed, the function can now be published to AWS.
- Open the Lambda project created earlier in Visual Studio.
-
Right click on the Project Name and select Publish to AWS Lambda
- If this is the first time Lambda is being published, an account profile will need to be used with the Access Keys from AWS. More information on this can be found at Managing Access Keys for IAM Users
- Select the Account profile to use and Region
- Ensure the Lambda Runtime is set to .NET 6
- Fill in the Function Name and click Next
- Change the Memory (MB) to 1024
- Choose a Role Name from the dropdown and then click Upload
This will run dotnet publish on the project and then zip up the files and dependencies and upload it to Lambda.
Change the Settings
Once the package is uploaded, the LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment variable of the function needs to be updated in order to properly load the dependencies.
- In the function page on the console, select the Configuration tab
- Click the Environment Variables tab then click Edit
- Click Add environment variable
- For the key, input
LD_LIBRARY_PATHand for the value input/tmp -
Click Save to save these changes
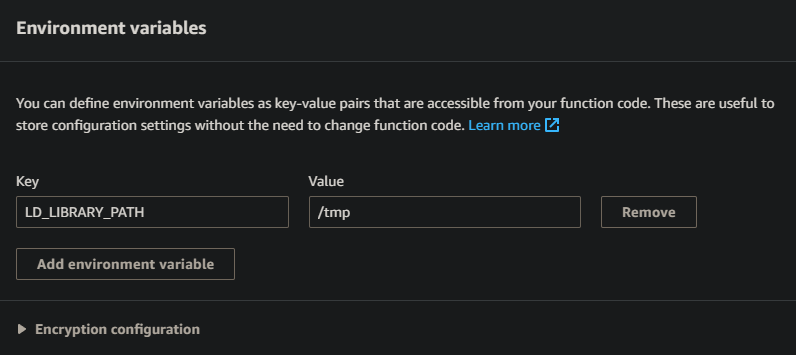
Once the environment variables are set, the layers need to be added to the function.
- In the function page on the console, expand Function overview
- Select Layers
- In the now open Layers section at the bottom, select Add a layer
- Choose Select from list of runtime compatible layers radio button
- In the Name dropdown, select the
lead-deps-layer - In the Version dropdown, select the most recent version number
-
Click Add to add this layer to the function
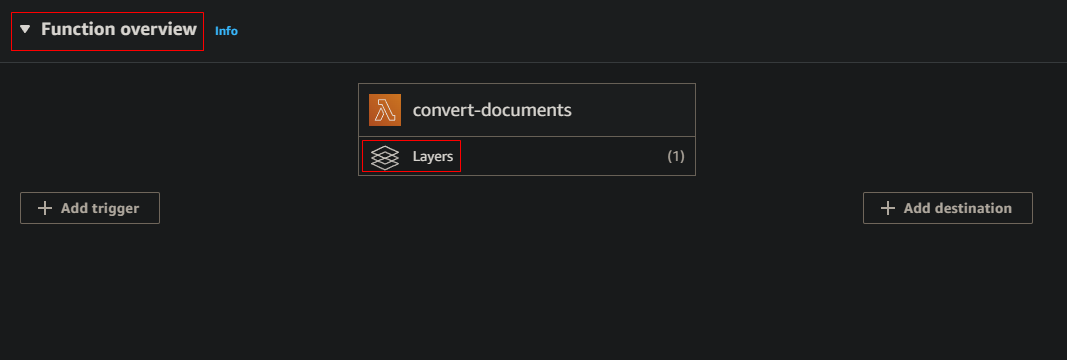
Test the Function
Once the previous step is completed, the function is ready to be tested.
-
In the function page on the console, select Test in the top right
- This will open the Configure test event dialog
- Choose the
hello-worldEvent Template - Fill in the Event name
- Replace the json with the following:
{"InputUrl": "https://demo.leadtools.com/images/tiff/ocr1.tif","DocumentFormat": 1}
-
Click Test to run the test event
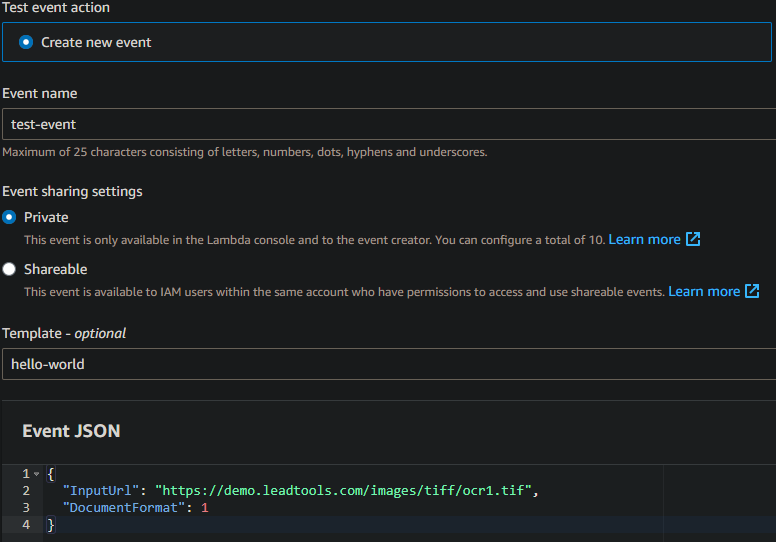
If everything was setup correctly, the Execution results should return succeeded and look something like:
Wrap-up
This tutorial showed how to create a new AWS Lambda function, gather the needed dependencies, and publish it to AWS.
