Queue - C# .NET 6
This tutorial shows how to queue tasks using the LEADTOOLS Cloud Services in a C# .NET 6 console application.
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Summary | This tutorial covers how to make Queue requests and process the results using the LEADTOOLS Cloud Services in a C# .NET 6 console application. |
| Completion Time | 30 minutes |
| Project | Download tutorial project (2 KB) |
| Platform | LEADTOOLS Cloud Services API |
| IDE | Visual Studio 2022 |
| Language | C# .NET 6 or higher |
| Development License | Download LEADTOOLS |
| Try it in another language |
|
Required Knowledge
Be sure to review the following sites for information about LEADTOOLS Cloud Services API.
- Create an Account and Application with the LEADTOOLS Hosted Cloud Services
- Introduction and Service Call Requirements
- Required Parameters and Return Objects
Application ID and Password
Create an Account with LEADTOOLS Hosted Cloud Services to obtain both Application ID and Password strings.
Service Plans
LEADTOOLS Service Plan offerings:
| Service Plan | Description |
|---|---|
| Free Trial | Free Evaluation |
| Page Packages | Prepaid Page Packs |
| Subscriptions | Prepaid Monthly Processed Pages |
To further explore the offerings, refer to the LEADTOOLS Hosted Cloud Services page.
To obtain the necessary Application ID and Application Password, refer to Create an Account and Application with the LEADTOOLS Hosted Cloud Services.
Create the Project and Add the Required Dependencies
In Visual Studio, create a new C# .NET 6 Console project, and add the following required NuGet package:
Newtonsoft.Json
Add the Queue Code
With the project created and the package added, coding can begin.
In the Solution Explorer, open Program.cs. Add the following statements to the using block at the top.
// Using block at the topusing Newtonsoft.Json;using Newtonsoft.Json.Linq;using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Net;using System.Net.Http;using System.Net.Http.Headers;using System.Text;using System.Threading.Tasks;
Add a string variable called hostedServicesUrl and an async Task called Queue().
The Queue task performs an UploadFile request to the LEADTOOLS Cloud Service API. If successful, a GUID will be returned for use later in the project.
private static string hostedServicesUrl = "https://azure.leadtools.com/api/";public static async Task Queue(){var client = InitClient();// If using URL to the filestring fileURL = "http://demo.leadtools.com/images/cloud_samples/ocr1-4.tif";string uploadUrl = string.Format("UploadFile?fileurl={0}", fileURL);var result = await client.PostAsync(uploadUrl, null);/*//If uploading a file as multi-part content:HttpContent byteContent = new ByteArrayContent(File.ReadAllBytes(@"path/to/file"));byteContent.Headers.ContentDisposition = new ContentDispositionHeaderValue("form-data"){Name = "attachment",FileName = "file-name"};var formData = new MultipartFormDataContent();formData.Add(byteContent, "formFieldName");string uploadUrl = "UploadFile";var result = await client.PostAsync(uploadUrl, formData);formData.Dispose();*/if (result.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.OK){//Unique ID returned by the servicesstring id = await result.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();Console.WriteLine("Unique ID returned by the services: " + id);await CheckFileForVerification(id, client);}elseConsole.WriteLine("Request failed with the following response: " + result.StatusCode);}
In this example we will first queue up an ExtractText request using the GUID that was returned from the UploadFile request in the Queue task.
After verifying the ExtractText request is queued, we will queue up a Convert request to convert the file to TIFF.
Create method private static async Task QueueExtractText(string id, HttpClient client) and method private static async Task QueueConversion(string id, HttpClient client) just under the Queue method.
private static async Task QueueExtractText(string id, HttpClient client){//The first page in the file to mark for processingint firstPage = 1;//Sending a value of -1 will indicate to the service that all pages in the file should be processed.int lastPage = -1;string recognitionUrl = string.Format("Recognition/ExtractText?firstPage={0}&lastPage={1}&guid={2}", firstPage, lastPage, id);var result = await client.PostAsync(recognitionUrl, null);if (result.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.OK)await QueueConversion(id, client);elseConsole.WriteLine("Request failed with the following response: " + result.StatusCode);}private static async Task QueueConversion(string id, HttpClient client){//The first page in the file to mark for processingint firstPage = 1;//Sending a value of -1 will indicate to the service that all pages in the file should be processed.int lastPage = -1;//Enum corresponding to the output format for the file. For the purposes of this script, we will be converting to tif.int fileFormat = 4;string conversionUrl = string.Format("Conversion/Convert?firstPage={0}&lastPage={1}&guid={2}&format={3}", firstPage, lastPage, id, fileFormat);var result = await client.PostAsync(conversionUrl, null);if (result.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.OK)await Run(id, client);elseConsole.WriteLine("Conversion Request failed to queue with the following response: " + result.StatusCode);}
With both QueueExtractText and QueueConversion queued we can process them with the Run request.
Note
This will mark the file as ready to be processed. Once a file has been marked for processing, or has finished processing, no further requests can be queued or run on that file.
Create the method private static async Task Run(string id, HttpClient client) and the method private static async Task CheckFileForVerification(string id, HttpClient client).
The CheckFileForVerification method is used by the Queue method to confirm the Upload request and initiate the QueueExtractText.
private static async Task Run(string id, HttpClient client){string uploadUrl = string.Format("Run?id={0}", id);var result = await client.PostAsync(uploadUrl, null);if (result.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.OK)await Query(id, client);elseConsole.WriteLine("Request failed with the following response: " + result.StatusCode);}private static async Task CheckFileForVerification(string id, HttpClient client){string queryUrl = string.Format("Query?id={0}", id.ToString());var result = await client.PostAsync(queryUrl, null);var returnedContent = await result.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();var returnedData = JObject.Parse(returnedContent);var fileStatus = (int)returnedData.SelectToken("FileStatus")!;if (fileStatus == 123){//The file is still being verified. We will check every half a second to make sure that the file has been verifiedawait Task.Delay(500);await Query(id, client);return;}if(fileStatus == 122)QueueExtractText(string id, HttpClient client);elseConsole.WriteLine("File failed verification with File Status: " + fileStatus);}
Next, create an async Task called Query(string id, HttpClient client), if successful, the response body will contain all the request data in JSON format.
private static async Task Query(string id, HttpClient client){string queryUrl = string.Format("Query?id={0}", id.ToString());HttpResponseMessage result;string returnedContent;JObject returnedData;int fileStatus;do{result = await client.PostAsync(queryUrl, null);returnedContent = await result.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();returnedData = JObject.Parse(returnedContent);fileStatus = (int)returnedData.SelectToken("FileStatus")!;//The file is still being processed -- we will sleep the current thread for 5 seconds before trying again.await Task.Delay(5000);} while (fileStatus == 100);Console.WriteLine("File has finished processing with return code: " + returnedData.SelectToken("FileStatus"));if ((int)returnedData.SelectToken("FileStatus")! != 200)return;ParseJson(returnedData.SelectToken("RequestData")!.ToString());}
Then, create the function ParseJson(string json) to process the returned JSON data.
private static void ParseJson(string json){JArray requestArray = JArray.Parse(json);foreach (var requestReturn in requestArray){Console.WriteLine("Service Type: " + requestReturn.SelectToken("ServiceType"));Console.WriteLine("Returned Data:");Console.WriteLine();if (requestReturn.SelectToken("ServiceType").ToString() == "Conversion"){var UrlArray = JArray.Parse(requestReturn.SelectToken("urls")!.ToString());foreach (var obj in UrlArray)Console.WriteLine(obj.ToString());}else{Console.WriteLine("Returned Data:" + requestReturn.SelectToken("data"));}Console.WriteLine("***********************************************");}}
Finally, create the function InitClient() to create a client connection to request the GUID and JSON data through.
Where it states Replace with Application ID and Replace with Application Password be sure to place your Application ID and Password accordingly.
private static HttpClient InitClient(){string AppId = "Replace with Application ID";string Password = "Replace with Application Password";HttpClient client = new HttpClient();client.BaseAddress = new Uri(hostedServicesUrl);client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Accept.Clear();client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Accept.Add(new MediaTypeWithQualityHeaderValue("application/json"));string authData = string.Format("{0}:{1}", AppId, Password);string authHeaderValue = Convert.ToBase64String(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(authData));client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Authorization = new AuthenticationHeaderValue("Basic", authHeaderValue);return client;}
Run the Project
In order to test run this code be sure to add Queue().GetAwaiter().GetResults(); to the static void Main section.
Run the project by pressing F5, or by selecting Debug -> Start Debugging.
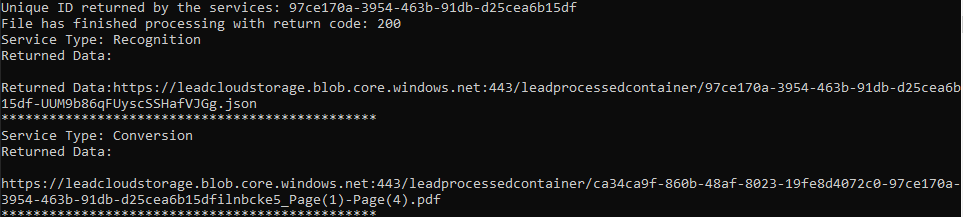
If the steps were followed correctly, the console appears and the application displays the JSON data results from the queued tasks.
Wrap-up
This tutorial showed how to queue tasks via the LEADTOOLS Cloud Services API.
