Load, Add, and Save Annotations - macOS Swift Console
This tutorial shows how to load, add, and save annotation objects in a macOS Swift Console application using the LEADTOOLS SDK.
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Summary | This tutorial covers how to load, add, and save annotations in a macOS Swift Console application. |
| Completion Time | 30 minutes |
| Visual Studio Project | Download tutorial project (5 KB) |
| Platform | macOS Swift Console Application |
| IDE | Xcode |
| Development License | Download LEADTOOLS |
| Try it in another language |
|
Required Knowledge
Get familiar with the basic steps of creating a project by reviewing the Add References and Set a License tutorial, before working on the Load, Add, and Save Annotations - macOS Swift Console tutorial.
Create the Project and Add LEADTOOLS References
Start with a copy of the project created in the Add References and Set a License tutorial. If you do not have that project, follow the steps in that tutorial to create it.
The references needed depend upon the purpose of the project. This tutorial requires the following Framework references located at <INSTALL_DIR>\LEADTOOLS22\Bin\Xcode\Frameworks\macOS:
Leadtools.frameworkLeadtools.Annotations.EngineLeadtools.Codecs.framework
Edit the Leadtools-Bridging-Header.h file to add the following imports:
#import <Leadtools.Annotations.Engine/Leadtools.Annotations.Engine.h> For a complete list of which files are required for your application, refer to Files to be Included in your Application.
Set the License File
The License unlocks the features needed for the project. It must be set before any toolkit function is called. For details, including tutorials for different platforms, refer to Setting a Runtime License.
There are two types of runtime licenses:
- Evaluation license, obtained at the time the evaluation toolkit is downloaded. It allows the toolkit to be evaluated.
- Deployment license. If a Deployment license file and developer key are needed, refer to Obtaining a License.
Note
Adding LEADTOOLS references and setting a license are covered in more detail in the Add References and Set a License tutorial.
Add the Load Annotations Code
With the project created, the references added, and the license set, coding can begin.
Using the Project Navigator, open main.swift. Below the call to the SetLicense() function, create a new instance of LTAnnCodecs.
Then, add a new function to your project named LoadAnnotations(codecs: LTAnnCodecs) -> LTAnnContainer?. This function takes in the LTAnnCodecs object created and will return an LTAnnContainer object containing the loaded LTAnnObjects. Be sure to call this new function below the LTAnnCodecs object creation as shown below.
SetLicense()let annCodecs: LTAnnCodecs = LTAnnCodecs()guard let annContainer: LTAnnContainer = LoadAnnotations(codecs: annCodecs) else { fatalError() }SaveAnnotations(codecs: annCodecs, container: annContainer)
Add the following code to the LoadAnnotations() function to load the annotation objects from file and return the LTAnnContainer. For the purposes of this tutorial, this sample Annotations XML File can be used.
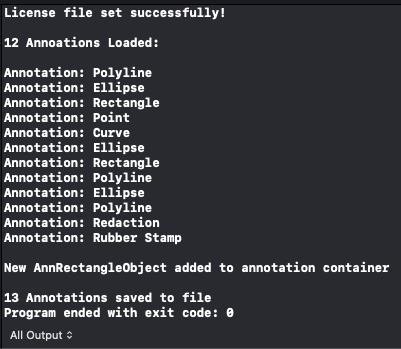
func LoadAnnotations(codecs: LTAnnCodecs) -> LTAnnContainer? {do {let xmlString = try String(contentsOfFile: "FILE PATH TO ANNOTATIONS XML", encoding: .utf8)// Load annotationsguard let annContainer: LTAnnContainer = codecs.load(from: xmlString, pageNumber: 1) else { fatalError("Failed to load file to container.") }// Print all the objects in the containerprint("\n\(annContainer.children.count) Annoations Loaded:\n")for i in 0..<annContainer.children.count {let object = annContainer.children[i]print("Annotation: \(object.friendlyName)")}return annContainer} catch {print(error.localizedDescription)}return nil}
Add and Save Annotations Code
Add a new function to your project named SaveAnnotations(codecs: LTAnnCodecs, container: LTAnnContainer). This function takes in the current LTAnnCodecs object and the LTAnnContainer returned from the LoadAnnotations() function. Be sure to call the SaveAnnotations() func below the call to the LoadAnnotations func, as shown in the previous section.
Add the code below to the SaveAnnotations() function to add a new LTAnnObject to the LTAnnContainer and then export the container to a new XML file.
func SaveAnnotations(codecs: LTAnnCodecs, container: LTAnnContainer) {// Add new rectangle to containerlet annRect: LTAnnRectangleObject = LTAnnRectangleObject()annRect.rect = LeadRectDMake(100, 200, 400, 400)annRect.stroke = LTAnnStroke.init(brush: LTAnnSolidColorBrush.init(color: "Red"), withThickness: LeadLengthD.init(value: 3.0))container.children.add(annRect)print("\nNew AnnRectangleObject added to annotation container\n")// Export annotations to XML filelet saveString = codecs.save(container: container, format: LTAnnFormat.annotations, data: nil, savePageNumber: 0)do {if let xml = try? XMLElement.init(xmlString: saveString) {let str = xml.xmlString(options: .nodePrettyPrint)try str.write(to: URL(fileURLWithPath: "FILE PATH TO EXPORT XML FILE"), atomically: true, encoding: .utf8)}} catch {print(error.localizedDescription)}print("\(container.children.count) Annotations saved to file")}
Run the Project
Clean the project to clear any errors by selecting Product -> Clean Build Folder or Shift + Command + K.
Run the project by selecting Product -> Run or Command + R.
If the steps were followed correctly, the application runs and loads the LTAnnContainer from the specified XML file, adds a new LTAnnRectangleObject to the LTAnnContainer, and then saves the modified container to a new XML file.
Wrap-up
This tutorial showed how to load and save annotation containers, as well as add an LTAnnObject to the LTAnnContainer. Also it covered how to use the LTAnnCodecs class.
