Queue Tasks - Java
This tutorial shows how to queue tasks using the LEADTOOLS Cloud Services in a Java application.
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Summary | This tutorial covers how to make Queue requests and process the results using the LEADTOOLS Cloud Services in a Java application. |
| Completion Time | 30 minutes |
| Project | Download tutorial project (8 KB) |
| Platform | LEADTOOLS Cloud Services API |
| IDE | IntelliJ |
| Language | Java |
| Development License | Download LEADTOOLS |
Required Knowledge
Be sure to review the following sites for information about LEADTOOLS Cloud Services API.
Application ID and Password
Create an Account with LEADTOOLS Hosted Cloud Services to obtain both Application ID and Password strings.
Service Plans
LEADTOOLS Service Plan offerings:
| Service Plan | Description |
|---|---|
| Free Trial | Free Evaluation |
| Page Packages | Prepaid Page Packs |
| Subscriptions | Prepaid Monthly Processed Pages |
To further explore the offerings, refer to the LEADTOOLS Hosted Cloud Services page.
To obtain the necessary Application ID and Application Password, refer to Create an Account and Application with the LEADTOOLS Hosted Cloud Services.
Create the Project and Add the Maven Dependency
In the IDE, create a new Java project with Maven, and add the following required Maven dependency to the pom.xml file:
<dependency><groupId>org.json</groupId><artifactId>json</artifactId><version>20210307</version></dependency>
Add the Queue Code
With the project created and the package added, coding can begin.
In Project Files, open App.java. Add the following import statements at the top.
import org.json.JSONArray;import org.json.JSONObject;import java.io.File;import java.io.FileNotFoundException;import java.net.URI;import java.net.http.HttpClient;import java.net.http.HttpRequest;import java.net.http.HttpRequest.BodyPublisher;import java.net.http.HttpResponse;import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;import java.util.Base64;import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;
Add a method named queue(). The queue() method sends a UploadFile request to the LEADTOOLS Cloud Services API. If successful a unique identifier (GUID) will be returned and then a query using this GUID will be made.
Add the code below to the queue() method.
private static void queue() {HttpClient client = HttpClient.newHttpClient();// If using URL to the fileString fileURL = "https://demo.leadtools.com/images/cloud_samples/ocr1-4.tif";String uploadUrl = String.format("UploadFile?fileurl=%s", fileURL);Results results = postAsync(uploadUrl, null, client);//If uploading a file as multi-part content:// File uploadFile = new File("path/to/file");// String uploadUrl = "UploadFile";// Results results = postAsync(uploadUrl, uploadFile, client);if (results.getStatusCode() == 200) {//Unique ID returned by the servicesSystem.out.println("Unique ID returned by the services: " + results.getData());checkFileForVerification(results.getData(), client);} else {System.out.println("Request failed with the following response: " + results.getStatusCode());}}
In this example we will first queue up an ExtractText request using the GUID that was returned from the UploadFile request in the queue task. After verifying that the ExtractText request is queued, we will queue up a Convert request to convert the file to PDF.
Create two new methods named queueExtractText(String id, HttpClient client) and queueConversion(String id, HttpClient client), beneath the queue() method. Add the code below to the queueExtractText() method.
private static void queueExtractText(String id, HttpClient client) {//The first page in the file to mark for processingint firstPage = 1;//Sending a value of -1 will indicate to the service that all pages in the file should be processed.int lastPage = -1;String recognitionUrl = String.format("Recognition/ExtractText?firstPage=%s&lastPage=%s&guid=%s", firstPage, lastPage, id);Results results = postAsync(recognitionUrl, null, client);if (results.getStatusCode() == 200) {queueConversion(id, client);} else {System.out.println("Request failed with the following response: " + results.getStatusCode());}}
Add the code below to the queueConversion() method. This method will be called inside the queueExtractText() method, as shown above.
private static void queueConversion(String id, HttpClient client) {//The first page in the file to mark for processingint firstPage = 1;//Sending a value of -1 will indicate to the service that all pages in the file should be processed.int lastPage = -1;//Enum corresponding to the output format for the file. For the purposes of this script, we will be converting to tif.int fileFormat = 4;String conversionUrl = String.format("Conversion/Convert?firstPage=%s&lastPage=%s&guid=%s&format=%s", firstPage, lastPage, id, fileFormat);Results results = postAsync(conversionUrl, null, client);if (results.getStatusCode() == 200) {run(id, client);} else {System.out.println("Conversion Request failed to queue with the following response: " + results.getStatusCode());}}
With both queueExtractText and queueConversion queued, we can process them with the Run request.
Note
This will mark the file as ready to be processed. Once a file has been marked for processing, or has finished processing, no further requests can be queued or run on that file.
Create two more methods named run(String id, HttpClient client) and checkFileForVerification(String id, HttpClient client). The run() method will be called inside the queueConversion() method, and the checkFileForVerification() method is called inside the queue method to confirm the Upload request and initiate queueExtractText.
Add the code below to the run() method.
private static void run(String id, HttpClient client) {String uploadUrl = String.format("Run?id=%s", id);Results results = postAsync(uploadUrl, null, client);if (results.getStatusCode() == 200) {query(id, client);} else {System.out.println("Request failed with the following response: " + results.getStatusCode());}}
Add the code below to the checkFileForVerification method.
private static void checkFileForVerification(String id, HttpClient client) {String queryUrl = String.format("Query?id=%s", id);Results results;JSONObject returnedData;int fileStatus = 0;do {try{results = postAsync(queryUrl, null, client);returnedData = new JSONObject(results.getData());fileStatus = returnedData.getInt("FileStatus");Thread.sleep(500);} catch (InterruptedException e) {//e.printStackTrace();}} while (fileStatus == 0 || fileStatus == 123);if (fileStatus == 122){queueExtractText(id, client);} else {System.out.println("File failed verification with the File Status: " + fileStatus);}}
Next, create a new method called query(String id, HttpClient client) that utilizes the GUID provided by the queueExtractText() method. If successful the response body will contain all the request data in JSON format. Be sure to call the query() method inside the run() method, as shown above. Add the code below to the query() method.
private static void query(String id, HttpClient client) {String queryUrl = String.format("Query?id=%s", id);Results results;JSONObject returnedData;int fileStatus = 0;do {try{results = postAsync(queryUrl, null, client);returnedData = new JSONObject(results.getData());fileStatus = returnedData.getInt("FileStatus");if (fileStatus != 200) Thread.sleep(5000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {returnedData = new JSONObject();//e.printStackTrace();}} while (fileStatus == 0 || fileStatus == 100 || fileStatus == 123);System.out.println("File has finished processing with return code: " + fileStatus);if (fileStatus != 200) {return;}parseJson(returnedData.get("RequestData").toString());}
Then, create two new methods named parseJson(String json) and postAsync(String path, File file, HttpClient client), which will both be called inside the query() method, as shown above.
Add the code below to the parseJson() method to process the returned JSON data.
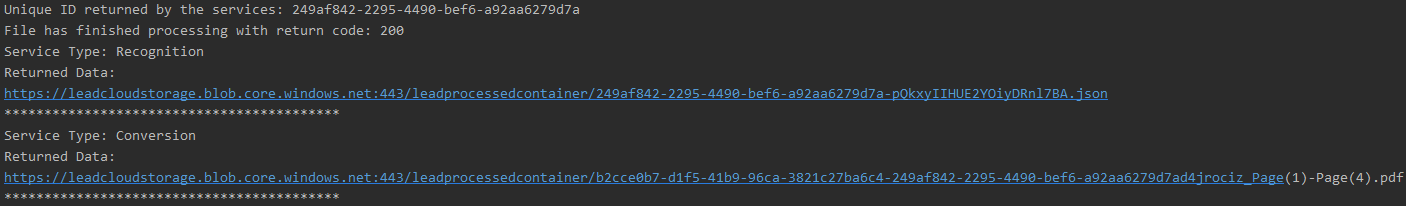
private static void parseJson(String json) {JSONArray requestArray = new JSONArray(json);for (Object requestObject : requestArray) {if (requestObject instanceof JSONObject) {JSONObject requestReturn = (JSONObject) requestObject;System.out.println("Service Type: " + requestReturn.getString("ServiceType"));System.out.println("Returned Data:");if (requestReturn.get("ServiceType").toString().equals("Conversion")) {JSONArray urlArray = new JSONArray(requestReturn.get("urls").toString());for (Object obj : urlArray) {System.out.println(obj.toString());}} else {System.out.println(requestReturn.get("data").toString());}System.out.println("******************************************");}}}
Add the code below to the postAsync() method to create a client connection to request the GUID and JSON data through. Where it states Replace with Application ID and Replace with Application Password be sure to place your Application ID and Password accordingly.
private static Results postAsync(String path, Object body, HttpClient client) {String AppId = "Replace with Application ID";String Password = "Replace with Application Password";String authHeader = "Basic " + new String(Base64.getEncoder().encode((AppId + ":" + Password).getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)));String hostedServicesUrl = "https://azure.leadtools.com/api/";BodyPublisher thisBody = HttpRequest.BodyPublishers.ofString("null");if (body instanceof BodyPublisher) {thisBody = (BodyPublisher) body;} else if (body instanceof File) {try {thisBody = HttpRequest.BodyPublishers.ofFile(((File) body).toPath());} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {//e.printStackTrace();}}HttpRequest request = HttpRequest.newBuilder().POST(thisBody).uri(URI.create(hostedServicesUrl + path)).header("Accept", "application/json").header("Authorization", authHeader).header("Content-Type", "text/plain").build();CompletableFuture<HttpResponse<String>> result = client.sendAsync(request, HttpResponse.BodyHandlers.ofString());Results results = new Results();results.setData("");results.setStatusCode(0);try{results.setData(result.thenApply(HttpResponse::body).get(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS));results.setStatusCode(result.thenApply(HttpResponse::statusCode).get(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS));} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException | TimeoutException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return results;}
The application will require a helper class to store the results of the POST requests. Create a new class called Results and add the code below to it.
private static class Results {private String data;private int statusCode;public String getData() {return data;}public void setData(String data) {this.data = data;}public int getStatusCode() {return statusCode;}public void setStatusCode(int statusCode) {this.statusCode = statusCode;}}
Run the Project
In order to test run this code be sure to add queue(); to the static void main section.
Run the project by pressing Alt + F5, or by selecting Run -> Debug App.
If the steps were followed correctly, the console appears and the application displays the JSON data results from the queued tasks.
Wrap-up
This tutorial showed how to queue tasks via the LEADTOOLS Cloud Services API in a Java application.
