Implement LEADTOOLS with Discord - Python
This tutorial shows how to implement a Discord bot in discord.py using the LEADTOOLS SDK.
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Summary | This tutorial covers how to use the LEADTOOLS SDK in a discord.py bot application |
| Completion Time | 30 minutes |
| Visual Studio Project | Download tutorial project (3 KB) |
| Platform | Python Console Application |
| IDE | Visual Studio 2022 |
| Runtime Target | Python 3.10 or Higher |
| Development License | Download LEADTOOLS |
Required Knowledge
Get familiar with the basic steps of creating a project by reviewing the Add References and Set a License tutorial and the basics of creating a discord.py bot, before working on the Implement LEADTOOLS with Discord - Python tutorial.
Disclaimer
discord.py is an open-source Python API for Discord applications.
Refer to GitHub's discord.py license for their terms of use. discord.py license is separate from LEADTOOLS licensing. To obtain a LEADTOOLS SDK license, refer to Setting a Runtime License.
Create the Project and Add the LEADTOOLS References
Start by following the discord.py quickstart guide. The references needed depend upon the purpose of the project.
This tutorial requires the following .NET DLLs:
Leadtools.dllLeadtools.Codecs.dllLeadtools.Barcode.dll
For a complete list of which DLL files are required for your application, refer to Files to be Included With Your Application.
Set the License File
The License unlocks the features needed for the project. It must be set before any toolkit function is called. For details, including tutorials for different platforms, refer to Setting a Runtime License.
There are two types of runtime licenses:
- Evaluation license, obtained at the time the evaluation toolkit is downloaded. It allows the toolkit to be evaluated.
- Deployment license. If a Deployment license file and developer key are needed, refer to Obtaining a License.
Add LEADTOOLS References
Ensure that the LEADTOOLS pip package is installed by entering the following command in the Command Prompt:
pip install leadtoolsWith the project created, the references added, and the license set, coding can begin.
In the Solution Explorer, open Project-Name.py and place the following at the top of Project-Name.py.
import sys# Import LEADTOOLS Demo common modulessys.path.append("C:/LEADTOOLS22/Examples/Common/Python")from DemosTools import *from UnlockSupport import Supportimport discordfrom discord import app_commands# Add reference to LEADTOOLSfrom leadtools import LibraryLoaderLibraryLoader.add_reference("Leadtools")from Leadtools import *LibraryLoader.add_reference("Leadtools.Codecs")from Leadtools.Codecs import *LibraryLoader.add_reference("Leadtools.Barcode")from Leadtools.Barcode import *from System import *from System.Text import *
Setting the LEADTOOLS license
In the on_ready() method add the following:
await tree.sync(guild=discord.Object(id=<REPLACE WITH GUILD ID>))Support.set_license("<INSTALL DIR>/LEADTOOLS22/Support/Common/License")
Next, add support for slash commands by adding the following below the client = discord.Client(intents=intents) line:
tree = app_commands.CommandTree(client)
Read Barcodes From Uploaded Files
Add a new slash command that takes an image as an argument and outputs the content of any barcodes detected within the image.
Add the following method to the "Project-Name.py" file.
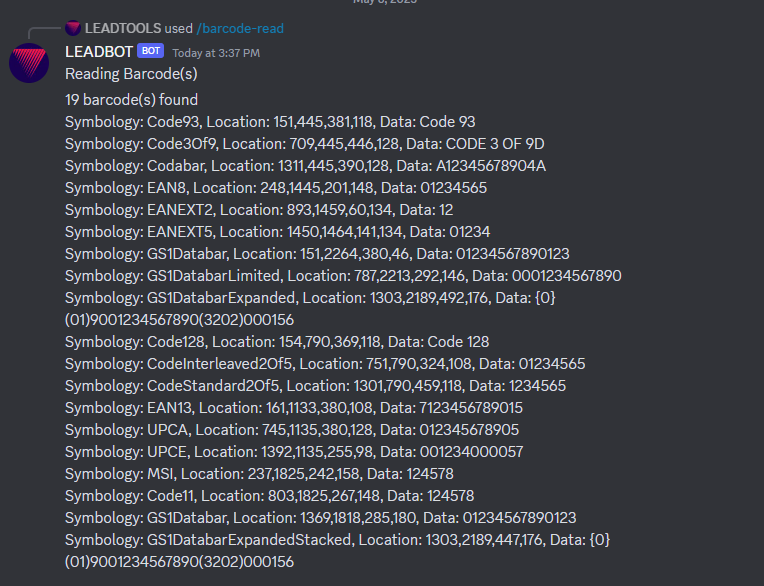
@tree.command(name = "barcode-read", description = "Reads any barcodes in an attached image", guild=discord.Object(id=<REPLACE WITH GUILD ID>))async def barcode_read(interaction, arg1: discord.Attachment):await interaction.response.send_message("Reading Barcode(s)")codecs = RasterCodecs()uri = Uri(arg1.url)image = codecs.Load(uri)barcode_engine_instance = BarcodeEngine()data_array = barcode_engine_instance.Reader.ReadBarcodes(image.Result, LeadRect.Empty, 0, None)sb = StringBuilder()sb.AppendFormat(f"{data_array.Length} barcode(s) found")sb.AppendLine()for i in range(data_array.Length):data = data_array[i]sb.AppendFormat("Symbology: {0}, Location: {1}, Data: {2}", data.Symbology, data.Bounds, data.Value)sb.AppendLine()await interaction.channel.send(sb.ToString())
Run the Project
Run the project by pressing F5, or by selecting Debug -> Start Debugging. If the steps were followed correctly, the application runs and adds a new read-barcode slash command to a discord bot.
Wrap-up
This tutorial showcases how to implement the LEADTOOLS barcode SDK with a discord.py application. The downloadable project for this tutorial includes commands to OCR text, apply image processing commands, read barcodes, and convert files.
